🧠 1. Why Do We Need OOP?
Think of coding a school management system with students, teachers, and courses. Without OOP, all data and logic get tangled in one giant file — a nightmare to maintain, update, or reuse!
✅ OOP Solves This By:
Groups code into logical objects
Reuse code across projects
Protects data from misuse
Easy to extend and maintain
🏪 Analogy: A Supermarket
Without OOP, it’s like throwing all groceries into one bag. With OOP, you organize items into sections (fruits, dairy, etc.), making it easier to find, manage, and add new items.
💡 2. What is OOP?
A programming style that uses classes and objects to model real-world entities, making code more structured and intuitive.
🏠 Real-World Analogy
Imagine a toy factory:
- Class: Blueprint for a toy (e.g., a robot design).
- Object: Actual toys made from the blueprint (e.g., a red robot, a blue robot).
OOP lets you define blueprints (classes) and create real items (objects) that can have unique traits and behaviors.
📦 3. What is a Class?
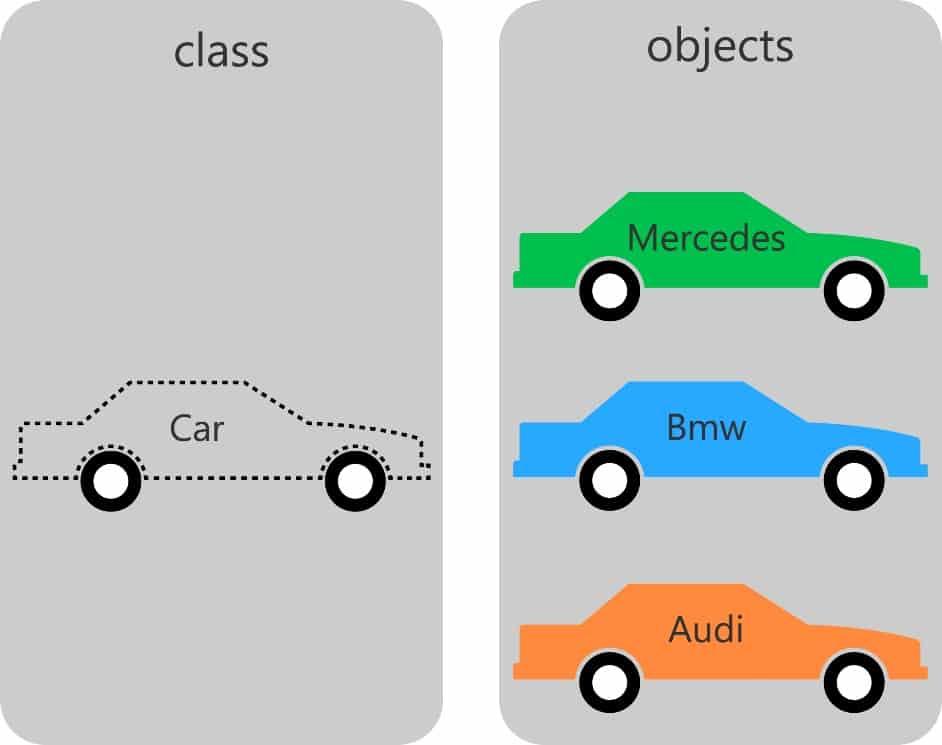
🧱 4. What is an Object?
✅ Java Code Example:
// Class: Car blueprint
class Car {
String color;
int speed;
void drive() {
System.out.println("Driving at speed: " + speed);
}
}
// Main class to create and use objects
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car myCar = new Car(); // Object creation
myCar.color = "Red";
myCar.speed = 100;
System.out.println("Car color: " + myCar.color);
myCar.drive();
}
}💬 Output:
Car color: Red
Driving at speed: 100
🔐 5. What is Encapsulation?
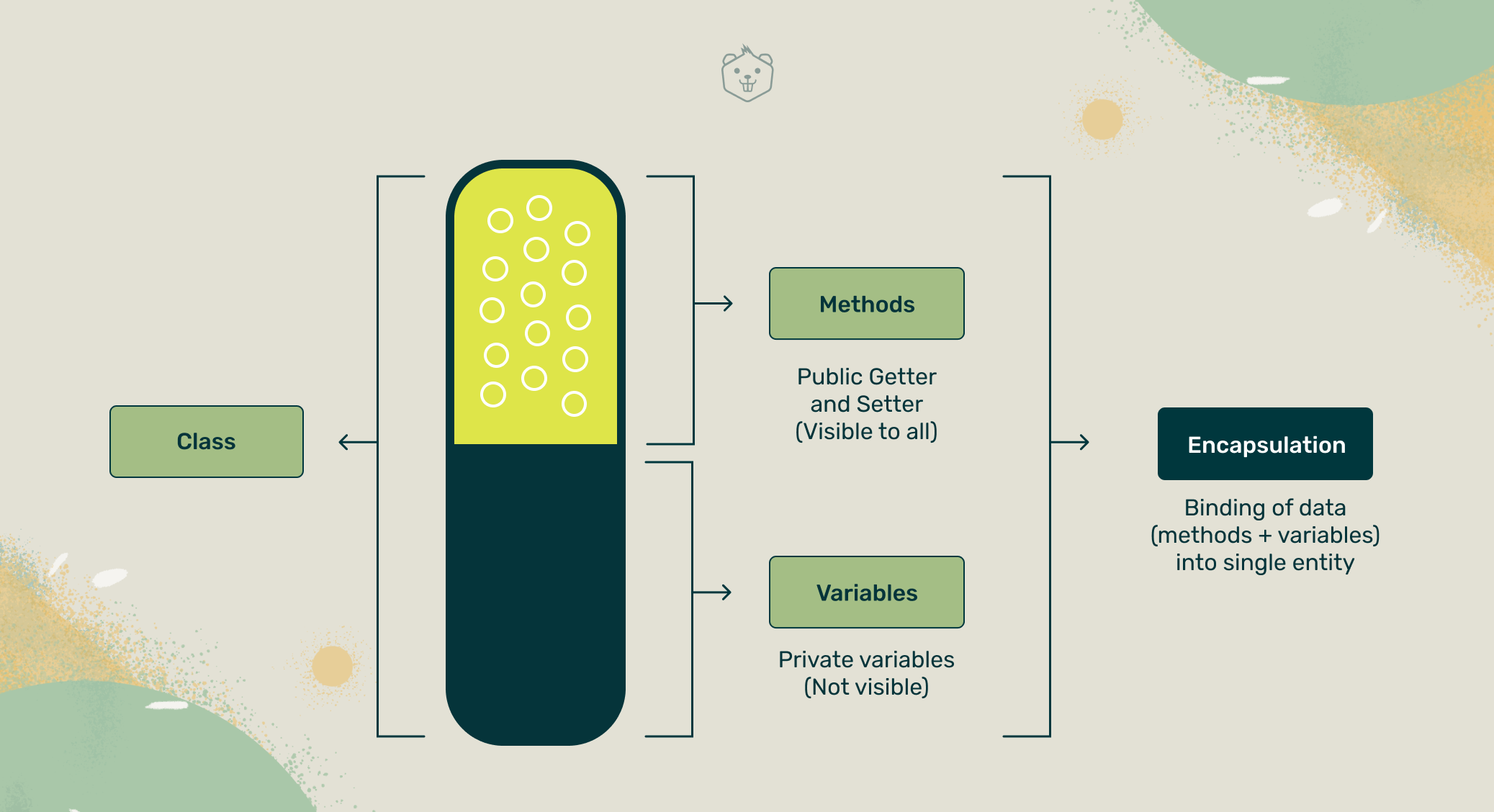
🔒 Analogy: A Safe
Your money (data) is locked in a safe (class). You can only access it with a key (methods like getters/setters), keeping it secure from outsiders.
✅ Java Code Example:
class BankAccount {
private double balance; // Hidden data
public void deposit(double amount) {
if (amount > 0) {
balance += amount;
System.out.println("Deposited: " + amount);
}
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BankAccount account = new BankAccount();
account.deposit(500.0);
System.out.println("Balance: " + account.getBalance());
}
}💬 Output:
Deposited: 500.0
Balance: 500.0
🧰 7. What are Access Modifiers?
Access modifiers control who can access a class, method, or variable.
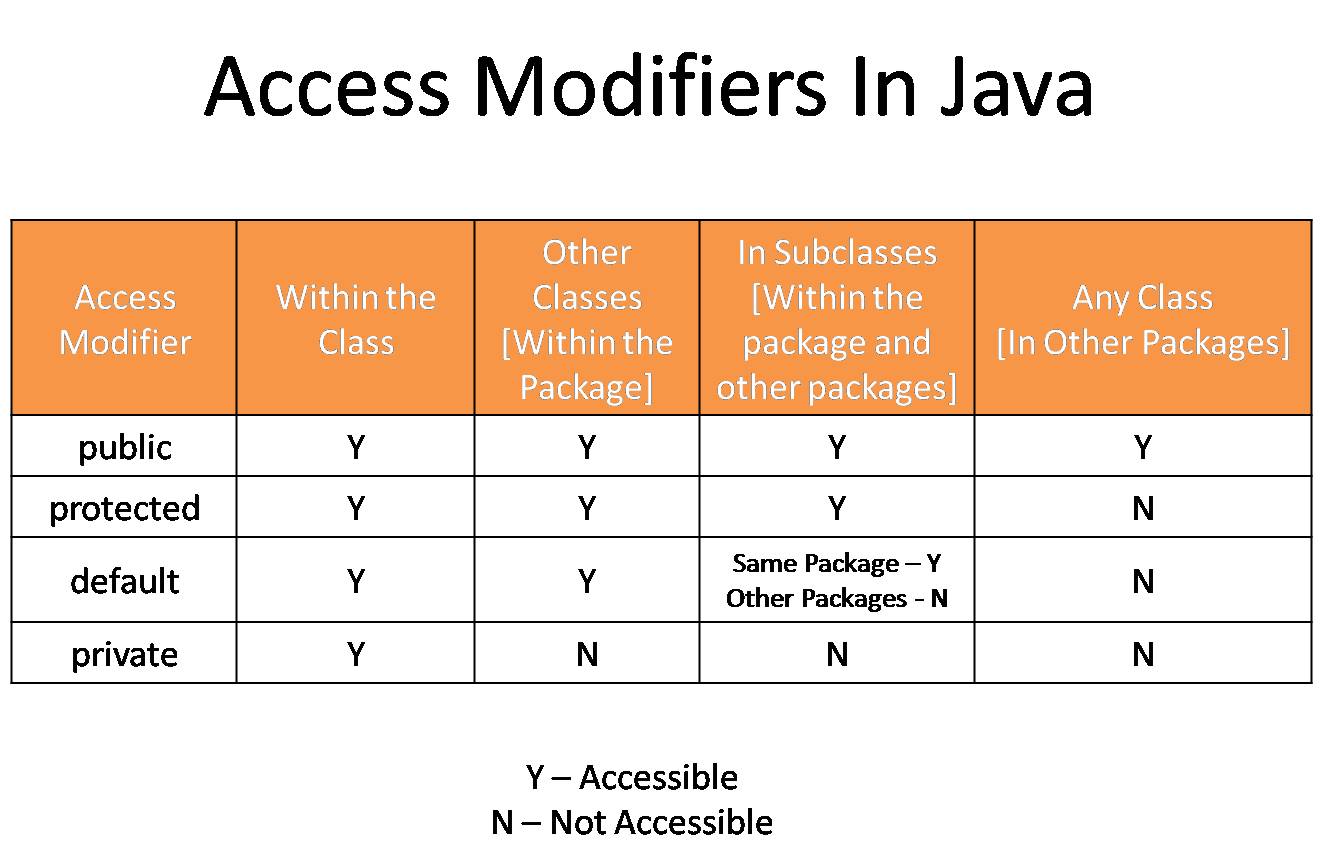
🛠 8. Getter and Setter Methods
private variables are hidden from outside access. Getters (to read) and setters (to update) provide controlled access.
✅ Java Code Example:
class Student {
private String name; // Hidden variable
// Setter with validation
public void setName(String n) {
if (n != null && !n.isEmpty()) {
name = n;
}
}
// Getter
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();
s.setName("Deepak");
System.out.println("Student name: " + s.getName());
}
}💬 Output:
Student name: Deepak
📌 9. Summary of Key OOP Concepts
| Term | Simple Meaning | Real-Life Example |
|---|---|---|
| Class | Blueprint for objects | Car design blueprint |
| Object | Real instance of a class | Your red car |
| Encapsulation | Hides data, uses methods for access | ATM hiding its code |
| Abstraction | Shows only essential features | Smartphone "Call" button |
| Private | Access within class only | Secret locker key |
| Public | Access from anywhere | TV remote |
| Getter/Setter | Read/write private data | ATM balance check |
🎯 10. Interactive Quiz
Test Your Understanding!
1. What is a class?
- A real instance of an object
- A blueprint for creating objects
- A method to hide data
- A type of variable
Answer: A blueprint for creating objects
2. What does encapsulation do?
- Exposes all data publicly
- Hides data and provides controlled access
- Creates multiple objects
- Simplifies complex code
Answer: Hides data and provides controlled access
3. Why use a getter method?
- To modify private data
- To read private data safely
- To create new objects
- To hide methods
Answer: To read private data safely
4. What is abstraction?
- Hiding data with private modifiers
- Showing only essential features
- Creating multiple classes
- Reusing code across classes
Answer: Showing only essential features
💬 11. Real Interview Questions
| Question | How to Answer | Tip |
|---|---|---|
| What are the main principles of OOP? | Encapsulation, Abstraction, Inheritance, and Polymorphism. Explain each briefly with examples (e.g., encapsulation as hiding data in a class). | Use real-world analogies like an ATM for encapsulation. |
| Explain the difference between a class and an object. | A class is a blueprint (e.g., a house design), while an object is an instance (e.g., an actual house built from the design). | Give a code example to show creation of an object. |
| Why is encapsulation important? | It protects data from unauthorized access and ensures controlled modification, improving security and maintainability. | Mention getters/setters and a real-world example like a bank vault. |
| What is abstraction, and how is it achieved? | Abstraction hides complex details and shows only necessary features. Achieved using abstract classes or interfaces in Java. | Use the smartphone analogy and mention interfaces. |
| Can you explain access modifiers with examples? | Describe public, private, protected, and default. E.g., private hides data within a class, public allows universal access. |
Show a code snippet with different modifiers. |
| Write a program demonstrating encapsulation. | Show a class with private variables, getters, setters, and validation (e.g., the BankAccount example above). | Explain why validation in setters is useful. |
| What happens if you don’t use access modifiers? | Variables/methods get default (package-private) access, accessible only within the same package. |
Clarify the risks of exposing sensitive data. |
✅ 12. Practice Tasks
Task 1: Implement a BankAccount Class
Create a BankAccount class with:
- Private
balance deposit(amount)method (only positive amounts)withdraw(amount)method (check sufficient balance)getBalance()method
Solution:
class BankAccount {
private double balance;
public void deposit(double amount) {
if (amount > 0) {
balance += amount;
System.out.println("Deposited: " + amount);
} else {
System.out.println("Invalid deposit amount");
}
}
public void withdraw(double amount) {
if (amount > 0 && amount <= balance) {
balance -= amount;
System.out.println("Withdrawn: " + amount);
} else {
System.out.println("Invalid or insufficient funds");
}
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BankAccount account = new BankAccount();
account.deposit(1000);
account.withdraw(500);
System.out.println("Final Balance: " + account.getBalance());
}
}💬 Output:
Deposited: 1000
Withdrawn: 500
Final Balance: 500
Task 2: Create a Student Class
Design a Student class with private fields for name and grade, getters/setters with validation, and a method to display student info.
Challenge: Ensure grades are between 0 and 100.